需求 使-不能成为换行的依据,除非该单词超长到一行装不下才可以让-出现在一行的开头或结尾。
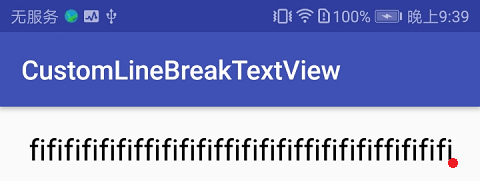
实现效果
实现过程 Word 类 用于保存单词内容、宽度、高度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private class Word {private String text;private float width;private float height;private Word (String text, float width, float height) {this .text = text;this .width = width;this .height = height;
Line 类 用于保存一行中的 Word
1 2 3 private class Line {private ArrayList<Word> wordList = new ArrayList <>();
将字符串按自定义规则分成单词 遍历字符串中的每一个字符,如果该字符不是-,且不是在A~Z或a~z之间,则认为已识别到单词的结尾
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public void setText (CharSequence charSequence) {if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(charSequence)) {StringBuilder stringBuilder = null ;int length = charSequence.length();for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) {char c = charSequence.charAt(i);if (c != '-' && (c < 'A' || (c > 'Z' && c < 'a' ) || c > 'z' )) {if (stringBuilder != null ) {null ;else {if (stringBuilder == null ) {new StringBuilder ();if (stringBuilder != null ) {else {"TextUtils.isEmpty(charSequence)" );
重写 onMeasure 方法 1、获取实际可用的宽高
1 2 int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
2、清除缓存
1 2 3 lineList.clear();float usedWidth = 0 ;Line line = null ;
3、遍历已分成的单词列表,测量每个单词在指定的 paint 下所占用的宽度
1 float width = paint.measureText(word);
(1)如果已占用宽度加上该单词的宽度比实际可用的宽度小或相等,则将该单词添加到行中,并添加一个单词间距的宽度到已占用宽度上
1 2 3 4 5 if (line == null ) {new Line ();new Word (word, width, paint.getTextSize()));
(2)如果已占用宽度加上该单词的宽度比实际可用的宽度大,则封闭前一行,创建新行
1 2 lineList.add(line);new Line ();
同时判断当前这一个单词的宽度是否已经超过实际可用的宽度了,如果超过了,则按照实际可用宽度截取字符串到一行,最后剩余部分单独添加到新的一行,作为该行的第一个单词,并添加一个单词间距的宽度到已占用宽度上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (width > widthSize) {Word restWord = addWordListBySub(word, widthSize);if (restWord != null ) {new Line ();
否则,将该单词作为新行的第一个单词,并添加一个单词间距的宽度到已占用宽度上
1 2 3 4 5 else {new Word (word, width, paint.getTextSize()));
4、最后,可能剩余宽度不足一行的情况,将其封闭为一行
1 2 3 if (!lineList.contains(line)) {
5、计算实际占用的宽度和高度并使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 int totalWidth = widthSize + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();int totalHeight = 0 ;int lineListSize = lineList.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < lineListSize; i++) {0 ).height;1 ) * wordVerticalMargin;
一种提高获取被截取字符串索引的速度的方法 定义一个递归方法,传入的参数是单词和一行的最大宽度。当传入的单词经过测量后的宽度小于或等于一行的最大宽度时,即认为已完成所有单词的截取,结束递归,或者当传入的字符串为空串时,也会结束递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private Word addWordListBySub (String word, int widthSize) {if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(word)) {float width = getMeasuredWidth(word);if (width <= widthSize) {return new Word (word, width, getTextHeight());else {return null ;
当传入的单词经过测量后的宽度大于一行的最大宽度时,计算单词中一个字符大概占的宽度,使用一行的最大宽度除以该宽度可得大概能满足字符串截取后的长度刚好等于一行的宽度
1 2 3 4 float oneCharWidth = width / word.length();int index = (int ) (widthSize / oneCharWidth);String substring = word.substring(0 , index);float substringWidth = getMeasuredWidth(substring);
为了精确,继续对截取字符串所需的索引的值做逼近处理,当获取到宽度不大于一行的宽度的最大值后,截取字符串,将剩余子串继续进行递归。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int realIndex;if (substringWidth < widthSize) {0 , realIndex);else if (substringWidth > widthSize) {0 , realIndex);else {float realWidth = getMeasuredWidth(realSubstring);Line line = new Line ();new Word (realSubstring, realWidth, getTextHeight()));String restSubstring = word.substring(realIndex);return addWordListBySub(restSubstring, widthSize);
大概计算出位置后,再遍历查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 private int getMinSubstringWidthIndex (String word, int widthSize, int index) {for (int i = index + 1 , size = word.length(); i < size; i++) {String substring = word.substring(i);float width = getMeasuredWidth(substring);if (width > widthSize) {int minSubstringWidthIndex = i - 1 ;return minSubstringWidthIndex;return index;private int getMaxSubstringWidthIndex (String word, int widthSize, int index) {for (int i = index - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) {String substring = word.substring(i);float width = getMeasuredWidth(substring);if (width < widthSize) {int maxSubstringWidthIndex = i;return maxSubstringWidthIndex;return index;
重写 onDraw 方法 canvas 在绘制文本时,需要知道的是绘制结束的位置,也就是图中大概红点所表示的位置,其余从哪画、怎么画均交给 paint 处理
1、计算第一个 Y,后面的 Y 均在此基础上叠加
1 float totalY = getPaddingTop() - getViewTop();
2、遍历行,当行内文本需要居中时,计算一行中所有单词及单词间的间隔使用的宽度,将剩余宽度作为左端偏移量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 for (Line line : lineList) {float marginLeft = 0 ;if (mGravity == GRAVITY_CENTER) {float totalUsedWidth = 0 ;for (Word word : wordList) {1 ) * mWordHorizontalMargin;2 ;
3、在行中遍历单词,绘制完一个单词后,X 位置需要加上单词宽度和单词间的间距
1 2 3 4 5 6 float totalX = getPaddingLeft() + marginLeft;for (Word word : wordList) {
4、当一行绘制完后,Y 位置需要加上行高和行间距
1 2 totalY += wordList.get(0 ).height;
源码地址 CustomLineBreakTextView